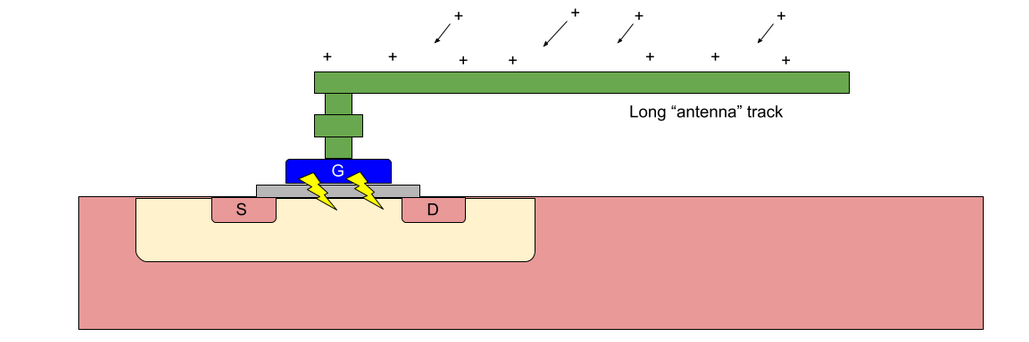
If long Metal interconnects is connected to the poly gate if the charged particles stored in the metal during fabrication is sufficient to break thin gate oxide, which will act as a Antenna and it will breakdown the gate oxide beneath the poly gate.
Antenna Ratio =metal Area(am)/gate area(ag)
Preventions:
1)metal jumper:-
2)diode insrtion
3)dummy mos device.
To minimize the mismatch of the device parameters that is called matching
(or)
To minimize the PVT variation
Interdigitation;
Here current will reflected to the near by device in which the gate terminals of all the device is shorted with drain and gate of source device.
Common centroid:
It gives 100% gradients matching.
Gradients:
Device should have same environment, same size, orientation,supply, temperature and location.
Latchup:
It is a failure mechanism in which a low resistance path between vdd and gnd, due to turn on the parasitic BJTS.
Prevention's:
Guard ring and Tap ring
Guard ring:
guard ring is need for protecting the noise to the devices from all sides like Diff pair and Current mirror.
current increases when Resistance Decreases.
Shielding:
To avoid the cross coupling occurrence due to high frequency signals passing beside the critical signal.
1) side shielding
2)Coaxial shielding
we need to shield low frequency net, if you shield high frequency net like clk is might add some cap which might slow it down.
ESD:
It is the sudden flow of static electric charge from one object to IC.
prevention:
All the input and output pins must have back to back esd diode connected to the Bond Pad.
Human body Model:
mainly concentrates, when human touch the IC pins there would be sudden charge flow from human body to chip by using diodes to fix the human body event.
Charge Device Model:
Chip will be between two parallel plates and charges, in this scenerio all layers in chip will get charges. this charge has to be discharge through any pin of the chip.
in this path there would be circuit whose gates connected to pad to protect these gate oxides we need to place CDM devices very close to gates.
Substrate noise:
Current leakage due to Dynamic switching circuits.
Using guard ring to avoid it.
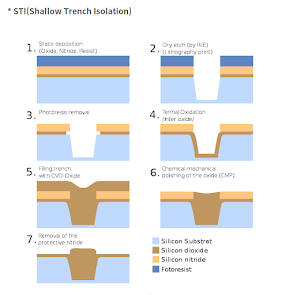
STI:
It prevents leakage between two adjucent semiconductor devices is called sti.
LOD:
It is mainly occurs due to the shallow trench isolation(STI). while doing sti some mechanical force will applies on nearest diffusion. due to this Vt will varied.
to avoid LOD Effect can Add Dummy to the active devices.
Reduce the vt:
reducing the oxide thickness & by reducing the channel length. threshold voltage is reduced by incrasing the body and drain voltage we can also reduce Vt.
EM:
Gradual displacement of atoms in a conductor due to flow of electrons with high current densities.
Prevention's:
increase metal width
metal stack
by avoiding 90 degrees Bendings.
IR Drop:
Every metal have some resistance. due to the resistance of that metal voltage drop will occur, this is called Voltage or IR drop.
Preventions:
increase metal width
metal stack
using higher metal.
WPE:
During ion implantation, ions gets scattered at near photo resist edges and stored at well edges.
which makes more concentration at edges.
Using dummies at edges.
Vt:
minimum voltage required to create channel in mosfet.
Body effect :
source and bulk should be at same potential ,If we didnt connected to same potential threshold voltage will vary for particular device.
- The change in the threshold voltage of a MOSFET, because of the voltage difference between body and source is called body effect
Cross talk:
Switching of the signal in one net can interfere neighbouring net due to crosscoupling capacitance it is known as crosss talk.
Preventions
Double spacing ,
multiple vias
Channel length modulation:
It can be define as he change or reduction in length of the channel(L) due to increase in the drain to source voltage in the saturation region.
Channel length modulation:
- The channel length of the MOSFET is changed due to the change in the drain to source voltage.
- This effect is called as the channel length modulation.
What is a capacitor?
What Is a MOSFET?
Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect Transistors commonly known as MOSFETs are electronic devices used to switch or amplify voltages in circuits. It is a voltage controlled device and is constructed by three terminals. The terminals of MOSFET are named as follows:
- Source
- Gate
- Drain
- Body
Depletion Mode
When there is no voltage across the gate terminal, the channel shows maximum conductance. When the voltage across the gate terminal is either positive or negative, then the channel conductivity decreases.
Enhancement Mode
When there is no voltage across the gate terminal, then the device does not conduct. When there is the maximum voltage across the gate terminal, then the device shows enhanced conductivity.
Operating Regions of MOSFET
A MOSFET is seen to exhibit three operating regions. Here, we will discuss those regions.
Cut-Off Region
The cut-off region is a region in which there will be no conduction and as a result, the MOSFET will be OFF. In this condition, MOSFET behaves like an open switch.
Ohmic Region
The ohmic region is a region where the current (IDS)increases with an increase in the value of VDS. When MOSFETs are made to operate in this region, they are used as amplifiers.
Saturation Region
In the saturation region, the MOSFETs have their IDS constant in spite of an increase in VDS and occurs once VDS exceeds the value of pinch-off voltage VP. Under this condition, the device will act like a closed switch through which a saturated value of IDS flows. As a result, this operating region is chosen whenever MOSFETs are required to perform switching operations.
What is a resistor?
Resistor is a passive two terminals electrical component used for regulating the flow of electricity in a circuit
sand to silicon
raw material sand primarily mad up of silicon dioxide
sand combined with carbon and heated to an extremely high temperate and remove the oxygen
metallurgical grad silicon
98% pure silicon
we need to 100% pure silicon
Siemens process
98% silicon and hydrochloride acid add with reactor and heated
99.9999% pure silicon
go for CZ ( Czochralski ) process
take furnace and add 99.9999% silicon combined with p type or n type importunity's add to furnace
in furnace mixing with silicon negates and type of impurities(trivalent or pentavalent ), sheet rode dip in furnace or crusable if crusable is rotating clockwise means, sheet rode will rotate anticlockwise direction, then we get ingot.
that ingot slices by using diamond then we get wafer by the chemical mechanical process smoothing the surface of wafer


Comments
Post a Comment